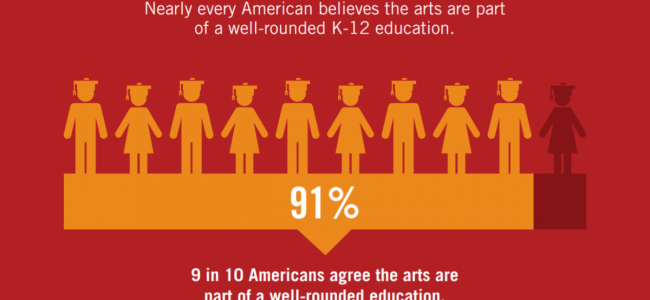
In the tapestry of education, the arts stand as vibrant threads, enriching the fabric of a well-rounded curriculum. From fostering critical thinking to promoting cultural understanding, the significance of arts education extends far beyond mere aesthetic appreciation. It is a transformative force that empowers students to navigate the complexities of life with imagination, empathy, and a deep appreciation for the human experience.
Through engaging activities and diverse mediums, arts education nurtures the cognitive, social, emotional, and cultural development of students. It ignites their creativity, enhances their problem-solving abilities, and cultivates their capacity for self-expression. By integrating the arts into the curriculum, we unlock a world of possibilities for students, empowering them to become well-rounded individuals who can contribute meaningfully to society.
Importance of Arts Education in Cognitive Development

Arts education plays a crucial role in cognitive development by enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Through hands-on experiences with various art forms, students learn to analyze, interpret, and synthesize information, fostering a deeper understanding of the world around them.
Fostering Creativity and Innovation
Art activities encourage students to experiment with different materials, techniques, and ideas. This experimentation promotes divergent thinking and allows students to develop original and innovative solutions to problems. By embracing the unknown and taking creative risks, they cultivate a mindset that values exploration and experimentation.
Developing Visual-Spatial Reasoning and Perception
Arts education emphasizes the development of visual-spatial reasoning, which involves the ability to perceive, interpret, and manipulate visual information. Through drawing, painting, and sculpting, students learn to observe and represent the world in two and three dimensions. This enhanced visual-spatial ability supports problem-solving in various domains, including mathematics, science, and engineering.
Arts Education and Social-Emotional Learning
Arts education plays a crucial role in fostering social-emotional learning by providing opportunities for self-expression, emotional regulation, empathy, cultural understanding, and self-esteem development.
Self-Expression and Emotional Regulation
Engaging in artistic activities allows students to express their emotions, ideas, and experiences in a safe and supportive environment. Through painting, music, dance, or drama, they learn to communicate their feelings and develop coping mechanisms for difficult emotions.
Empathy and Cultural Understanding
Arts education exposes students to diverse perspectives and cultures. By exploring different artistic traditions and styles, they develop an understanding of different cultures and learn to appreciate the richness of human expression. This fosters empathy and promotes tolerance.
Self-Esteem and Confidence
Success in artistic endeavors can boost students’ self-esteem and confidence. When they see their artistic creations come to life, they experience a sense of accomplishment and pride. This positive feedback loop encourages them to take risks and explore their creative potential.
Arts Education and Cultural Literacy
Arts education plays a crucial role in fostering cultural awareness and appreciation. Through exposure to various art forms, students gain insights into different cultures, their histories, values, and perspectives. This exposure fosters empathy, understanding, and respect for diverse cultures, promoting a sense of global citizenship.
Preserving and Transmitting Cultural Heritage
Arts education also serves as a means of preserving and transmitting cultural heritage. Traditional art forms, such as folk music, dance, and crafts, embody the collective experiences, beliefs, and traditions of a particular culture. By incorporating these art forms into the curriculum, schools can help preserve and pass on this rich cultural heritage to future generations.
Fostering a Deeper Understanding of Different Cultures
Arts education provides students with a window into the world’s diverse cultures. Through studying different art forms, such as music, literature, and visual arts, students learn about the unique perspectives, values, and traditions of various societies. This knowledge helps them develop a more nuanced understanding of the world and appreciate the richness of human experience.
Arts Education and Career Readiness
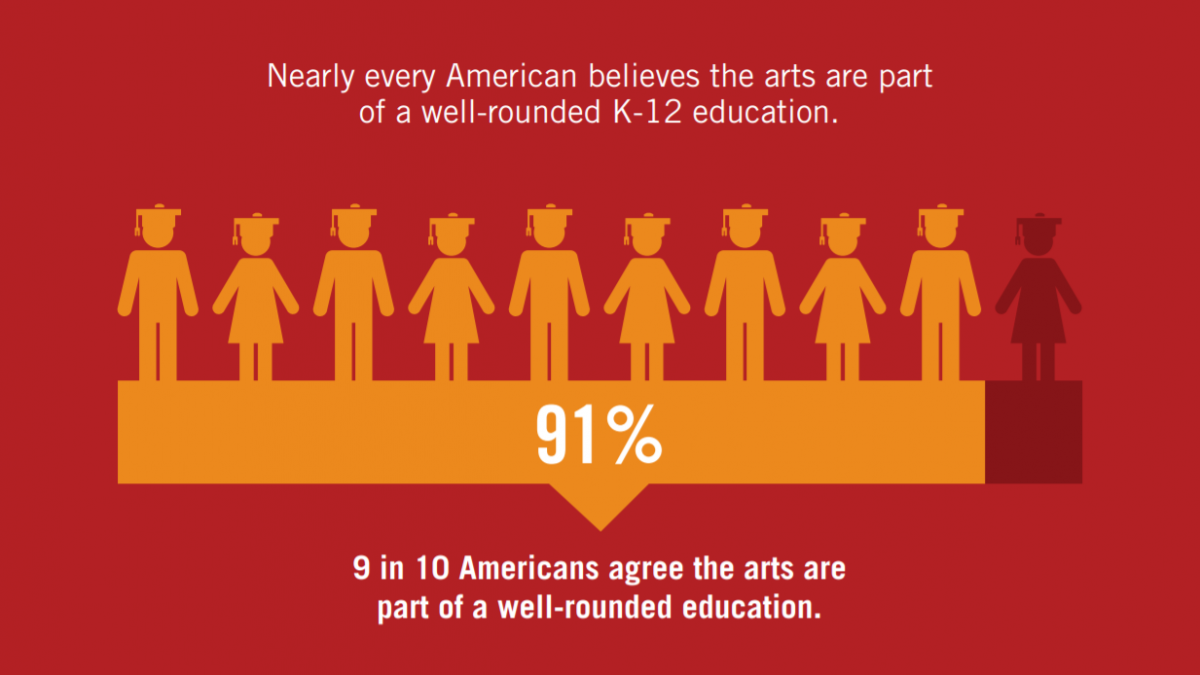
Arts education equips students with valuable transferable skills that are highly sought after in the modern workforce. Through hands-on experiences in various art forms, students develop essential abilities such as communication, collaboration, and project management.
Arts education fosters effective communication skills by providing students with opportunities to express themselves creatively and articulate their ideas. They learn to convey their thoughts and emotions through visual, auditory, and kinesthetic means, developing confidence in presenting their perspectives. Collaboration is another crucial skill nurtured through arts education.
Students work together on group projects, learning to share ideas, negotiate solutions, and support each other’s efforts. This collaborative environment mirrors the dynamics of many professional settings, preparing students to work effectively in teams.
Arts Education in Diverse Career Paths
The transferable skills gained through arts education extend beyond the arts sector. In fact, studies have shown that individuals with arts backgrounds excel in a wide range of careers, including technology, business, and healthcare. For instance, in the tech industry, arts education can enhance creativity, problem-solving, and user experience design.
In business, arts education fosters strong communication, presentation, and marketing skills. In healthcare, arts-based interventions have proven effective in promoting patient well-being and improving communication between patients and healthcare professionals.
Success Stories
Numerous successful individuals have attributed their professional achievements to the foundation they gained through arts education. Steve Jobs, the co-founder of Apple, credited his calligraphy classes with developing his attention to detail and appreciation for aesthetics, which influenced the design of Apple products.
Oprah Winfrey, the renowned talk show host and entrepreneur, emphasized the importance of drama classes in building her confidence and communication skills.
Integrating Arts Education into the Curriculum
Integrating arts education across different subject areas offers numerous benefits. It fosters creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. Arts-based activities enhance student engagement, making learning more enjoyable and meaningful.
Incorporating arts into science lessons can involve using dance to demonstrate chemical reactions or creating musical compositions based on scientific concepts. Math lessons can include designing geometric patterns or using music to teach fractions.
Strategies for Integrating Arts Education
- Identify natural connections between arts disciplines and other subjects.
- Plan collaborative projects involving multiple teachers.
- Use arts-based activities as assessment tools.
History lessons can be enriched through drama, where students enact historical events. Language arts can incorporate poetry, storytelling, and music to enhance reading comprehension and writing skills.
Examples of Successful Arts Integration Programs
- The Kennedy Center’s “Arts Integration Toolkit” provides resources and support for teachers.
- The “Teaching Through the Arts” program in New York City has shown improved student engagement and academic achievement.
Arts integration empowers students to express themselves creatively, connect with different cultures, and develop a lifelong appreciation for the arts.
Assessing Arts Education Outcomes
Assessing the outcomes of arts education can be challenging due to the subjective nature of the subject matter. However, there are several methods that can be used to evaluate student progress in the arts, including performance-based assessments and portfolios.
Performance-based assessments involve students demonstrating their skills and knowledge through a live performance. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as playing a musical instrument, singing a song, or acting in a play. Portfolios are collections of student work that can be used to assess their progress over time.
Portfolios can include a variety of items, such as drawings, paintings, sculptures, and writing samples.
Assessment data can be used to improve arts education programs and inform decision-making. For example, data from performance-based assessments can be used to identify areas where students need additional support. Data from portfolios can be used to track student progress over time and identify students who are at risk of falling behind.
Final Review
In conclusion, the importance of arts education in a well-rounded curriculum cannot be overstated. It is an investment in the future of our students, providing them with the skills, knowledge, and dispositions they need to thrive in a rapidly changing world.
By embracing the arts, we nurture the whole child, fostering their creativity, empathy, critical thinking, and cultural awareness. Let us continue to advocate for the integration of arts education into our schools and communities, ensuring that every student has the opportunity to experience the transformative power of the arts.
FAQ
Why is arts education important in schools?
Arts education is crucial in schools because it fosters creativity, critical thinking, problem-solving, empathy, cultural understanding, and self-expression. It also contributes to students’ overall academic achievement and well-being.
How can arts education be integrated into the curriculum?
Arts education can be integrated into the curriculum through various strategies, such as incorporating arts-based activities into science, math, history, and language arts lessons. It can also be taught as a standalone subject or through extracurricular programs.
What are the benefits of arts education for students?
Arts education provides numerous benefits for students, including enhanced cognitive development, improved social-emotional skills, increased cultural awareness, and preparation for future careers. It also contributes to students’ overall well-being and quality of life.

